CDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABCDEFGABC
Human hearing range
VOCAL
25 31 40 50 62 80 100 125 160 200 250 320 400 500 640 800 1K 1.3K1.6K 2K 2.5K 3.1K 4K 5K 6.2K 8K 10K 13K 16K 20K
Soprano
Contralto
Baritone
Bass
WOODWIND
Piccolo
Flute
Oboe
Clarinet in B flat orA
Clarinet in E flat
Bass Clarinet
Basset Hom
CorAnglais
Bassoon
Double Bassoon
BRASS
Soprano Saxophone
Alto Saxophone
Tenor Saxophone
Baritone Saxophone
BassSaxophone
Trumpet in C
Trumpet in F
Alto Trombone
Tenor Trombone
Bass Trombone
Tuba
Valve Hom
STRINGS
Violin
Viola
Cello
Double Bass
Guitar
KEYBOARDS
Pianoforte
Organ
PERCUSSION
Celesta
Timpani
Xylophone
FREQUENCY
25 31 40 50 62
80
100 125 160 200 250 320 400 500 640
800
1K
1.3K1.6K
2K
2.5K 3.1K
4K
5K
6.2K
8K
10K 13K 16K 20K
Mid C
10
5. APPLICATION
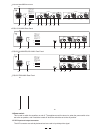
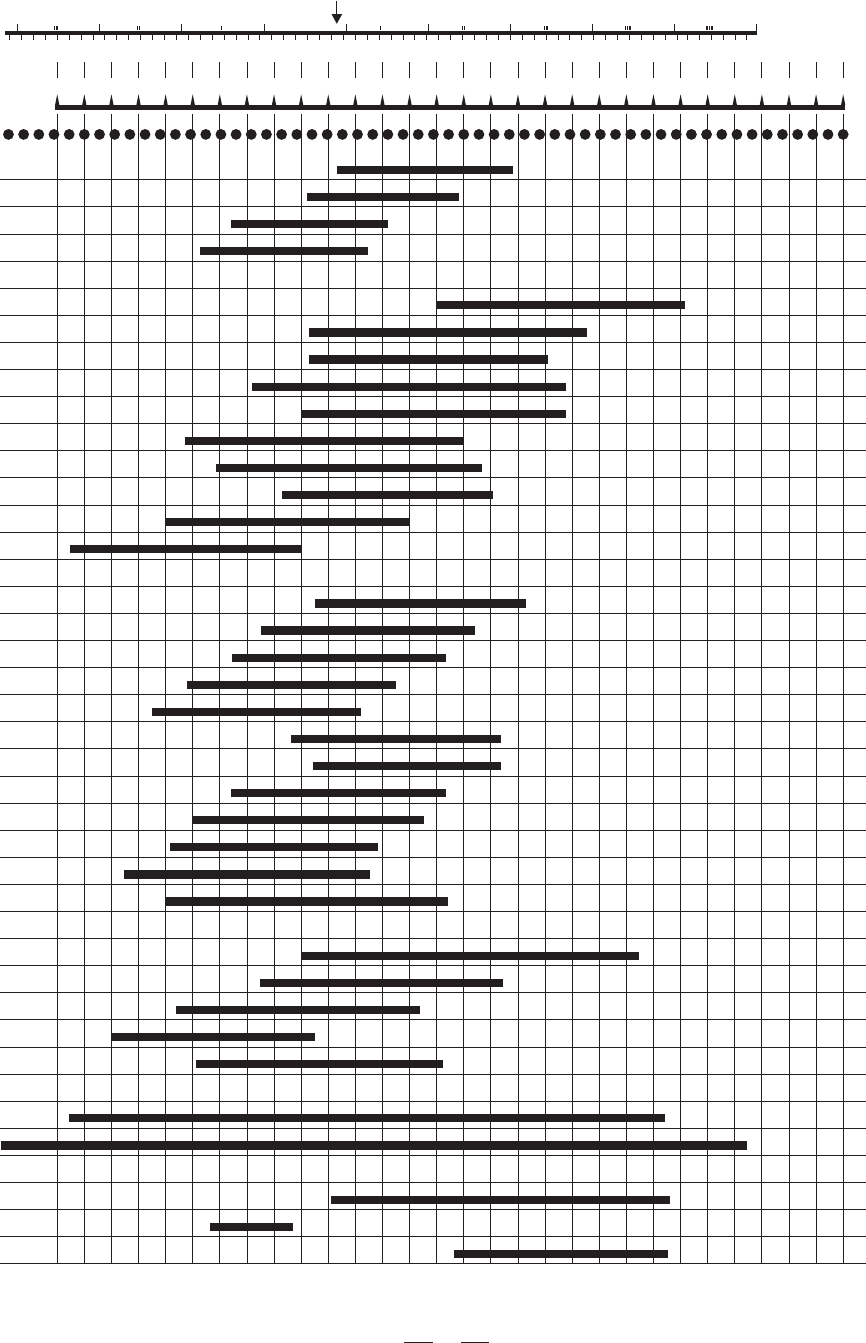
5.1 The Sound Frequency
Typical Frequency of Each Instrument and Voice
In recording studios as well as stage or radio plays, the EQU MKII Series Graphic Equalizer will be your valuable
sound tool to modify the frequency "contour" of a sound. But first of all, you should clarify the typical frequency of
each instrument and voice, so that you can obtain nice results in terms of sound characterization. The tables on
the following pages will give you an idea of specific frequencies and their acoustic significance.