4 - Principles of Operation
52
Two current shunt resistors monitor the output current. RmHi (R473) monitors the high current range; RmLo (R403)
monitors the low current range. Shunt clamps, connected in parallel across RmLo, turn on at approximately 25 mA to
limit the voltage drop at high currents. The Range_Select signal sets the level at which switching occurs. The output
of the current monitor drives the level.
The SCR, connected across the output, will fire and short the output when an overvoltage condition is detected. The
SCR is controlled by the OV_SCR* signal from the crowbar control circuit (described in the next section).
The output filter capacitor provides additional filtering of the dc output.
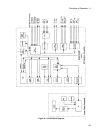
Control Circuits
As shown in Figure 4-2, the control circuits consist of the CV/CC controls, output voltage/current monitor, bias
supplies, and SCR control.
The CV/CC control circuits provide a CV control loop, a positive CC control loop, and a negative CC control loop.
For any value of load resistance, the supply must act either as a constant voltage (CV) or as a constant current (CC)
supply. Transfer between these modes is accomplished automatically by the CV/CC control circuit at a value of load
resistance equal to the ratio of the programmed voltage value to the programmed current value. The negative CC
control circuit is activated when a current source such as another power supply is connected across the output
terminals and its voltage is greater than the programmed voltage. A low level CV_Detect*, CC_Detect*, or
CCN_Detect* signal is returned to the secondary interface to indicate that the corresponding mode is in effect.
When the CV loop is in control, diode D328 is conducting current. Voltage regulation is accomplished by comparing
the programmed voltage signal CV_Prog with the output voltage monitor signal Vmon. The Vmon signal is in the 0
to +5 V range, which corresponds to the zero to full-scale output voltage range of the supply. If the output voltage
exceeds the programmed voltage, Vmon goes high and produces a more negative-going CV signal, which reduces
the input to the voltage gain stage and lowers the output voltage. Conversely, if the output voltage is less than the
programmed voltage, Vmon goes low and produces a more positive-going CV signal, which increases the input to
the voltage gain stage and raises the output voltage. Depending upon the position of the sense switch, the output
voltage is either monitored at the supply's output terminals (local), or at the load (remote) using the +S and -S
terminals with remote sense leads connected to the load. If the output voltage goes higher than the programmed
value, the unit starts sinking current to reduce the output voltage.
When the CC loop is in control, diode D325 is conducting current. Current regulation is accomplished by comparing
the programmed current signal CC_Prog with the output current monitor signal Imon_H. The Imon_H signal is
produced by measuring the voltage drop across the current monitoring resistor and is in the 0 to +5 V range, which
corresponds to the zero to full-scale output current range of the supply. If the output current exceeds the
programmed current, Imon_H goes high and produces a more negative going CC signal, which reduces the input to
the voltage gain stage and lowers the output current. Conversely, if the output current is less than the programmed
current, Imon_H goes low and produces a more positive-going CC signal, which increases the input to the voltage
gain stage and raises the output current.
When the supply is sinking current, only the CV control circuit or the CCN control circuit can be active. In this case,
the supply is acting as a load instead of a power source and will attempt to pull the output voltage down by drawing
off current from the externally applied source. The current that will be drawn from the externally supplied source is
determined by the CC_Prog signal. When the current required to reduce the voltage is less than the programmed
current value, the CV control circuit is active and regulates the output voltage. When the current required to reduce
the voltage exceeds the programmed current value, the CCN control circuit is active. It regulates the output current
by comparing the negative Imon_H signal to the inverted CC_Prog signal.
During operation, a PM_Inhibit signal will cause the turn-on control to turn off the bias to the voltage gain stage and
shut down the output if any of the following occur: