61
4. OPERATION continued …
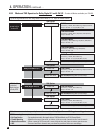
The Scale Output menu provides several options for making non-16:9 inputs, and 16:9 inputs that have shrunk
due to being matted (letterboxed) then pillarboxed, fit on a 16:9 screen. To quickly check what the source
component is putting out, select ‘No Scaling’, then make the appropriate selection.
Panoramic Stretch
Fills the screen by stretching only the sides of the picture. The middle portion stays undistorted. Use with 4:3
input if you don’t like seeing empty sides on a 16:9 screen.
Anamorphic Stretch
Fills the screen by stretching the whole picture sideways. Use this setting for DVDs that are anamorphic, or
“enhanced for widescreen TVs” as some DVD cases indicate when the source material has an aspect ratio
greater than 4:3. The images on these DVDs are squeezed sideways so that the full vertical resolution can
be used on the image instead of being wasted on recording a letterbox. The image then has to be stretched
back to normal to be displayed properly.
Letterbox and Pillarbox
With this setting, original aspect ratio is preserved, therefore parts of the screen are left empty. The shade
of the empty areas can be adjusted – see section 3.8.
Zoom
Intended for temporary close-up. Zoom Size is adjustable, and if it’s changed from the factory default (100),
Horizontal Position and Vertical Position become adjustable. Note that Zoom acts on the output, after
processing, and does not produce an image with as high quality as Custom Setting under Crop Input – Zoom
enlarges artifacts as well as the image whereas Crop Input discards the unwanted material before
processing, thus using the processor’s power towards the part of the frame that you want to view.
No Scaling
Scaling is bypassed – standard-def images normally shrink to center of screen. Intended for comparisons
during test and setup. Horizontal Size and Vertical Size adjusments remove the outsides of the image, and if
they’re changed from the factory defaults (100), Horizontal Position and Vertical Position become adjustable.
Examples of the most common aspect ratios:
The aspect ratio of a screen or image is the proportion of its width to its height.
1.33:1 (4:3)
SDTV, most PC
monitors
classic movies
1.78:1 (16:9)
HDTV, widescreen movies
movies also 1.66:1, 1.85:1
2.35:1
‘Scope’ movies
also 2.20:1, 2.40:1, 2.55:1
Panoramic Stretch
Anamorphic Stretch
Letter/Pillar Box
Zoom
No Scaling
SCALE OUTPICTURE CROP INPUT PATTERNS INFO
OUTPUT